6.10. Federated Learning and Label Flipping attacks#
In this notebook we train a machine learning model for MNIST classification. We then train the same model in a federated learning setting. In this setting, we test label flipping attacks and some defence mechanisms.
#IMPORTS
import sklearn
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,classification_report,confusion_matrix
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
import numpy as np
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
import copy
from time import sleep
from tqdm import tqdm
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import warnings
from sklearn.exceptions import ConvergenceWarning
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", category=ConvergenceWarning)
import ssl
ssl._create_default_https_context = ssl._create_unverified_context
mnist = fetch_openml('mnist_784')
X = mnist.data.to_numpy()
y = mnist.target.to_numpy()
# Normalize X to 0..1
X = X / 255.0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ModuleNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last)
File ~\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\_optional_dependencies.py:42, in check_pandas_support(caller_name)
41 try:
---> 42 import pandas # noqa
44 return pandas
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas'
The above exception was the direct cause of the following exception:
ImportError Traceback (most recent call last)
File ~\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\sklearn\datasets\_openml.py:1059, in fetch_openml(name, version, data_id, data_home, target_column, cache, return_X_y, as_frame, n_retries, delay, parser, read_csv_kwargs)
1058 try:
-> 1059 check_pandas_support("`fetch_openml`")
1060 except ImportError as exc:
File ~\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\_optional_dependencies.py:46, in check_pandas_support(caller_name)
45 except ImportError as e:
---> 46 raise ImportError("{} requires pandas.".format(caller_name)) from e
ImportError: `fetch_openml` requires pandas.
The above exception was the direct cause of the following exception:
ImportError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[2], line 4
1 import ssl
2 ssl._create_default_https_context = ssl._create_unverified_context
----> 4 mnist = fetch_openml('mnist_784')
5 X = mnist.data.to_numpy()
6 y = mnist.target.to_numpy()
File ~\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\_param_validation.py:216, in validate_params.<locals>.decorator.<locals>.wrapper(*args, **kwargs)
210 try:
211 with config_context(
212 skip_parameter_validation=(
213 prefer_skip_nested_validation or global_skip_validation
214 )
215 ):
--> 216 return func(*args, **kwargs)
217 except InvalidParameterError as e:
218 # When the function is just a wrapper around an estimator, we allow
219 # the function to delegate validation to the estimator, but we replace
220 # the name of the estimator by the name of the function in the error
221 # message to avoid confusion.
222 msg = re.sub(
223 r"parameter of \w+ must be",
224 f"parameter of {func.__qualname__} must be",
225 str(e),
226 )
File ~\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\sklearn\datasets\_openml.py:1072, in fetch_openml(name, version, data_id, data_home, target_column, cache, return_X_y, as_frame, n_retries, delay, parser, read_csv_kwargs)
1067 else:
1068 err_msg = (
1069 f"Using `parser={parser!r}` with dense data requires pandas to be "
1070 "installed. Alternatively, explicitly set `parser='liac-arff'`."
1071 )
-> 1072 raise ImportError(err_msg) from exc
1074 if return_sparse:
1075 if as_frame:
ImportError: Returning pandas objects requires pandas to be installed. Alternatively, explicitly set `as_frame=False` and `parser='liac-arff'`.
X, X_public, y, y_public = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.05, random_state=42)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
6.11. Testing a centralized model#
We train a Scikit-learn multilayer perceptron to stablish a baseline accuracy for our following experiments.
mlp = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(50,50,),
activation='relu',
solver='sgd',
batch_size=64,
learning_rate_init=0.001,
max_iter=100,
tol=0.0001,
shuffle=False,
verbose=True)
mlp.fit(X_train,y_train)
result = mlp.predict(X_test)
print('Accuracy :', accuracy_score(y_test,result))
print(classification_report(y_test,result))
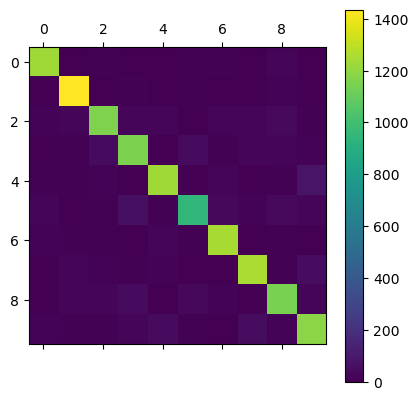
# BASELINE RESULTS
mat = confusion_matrix(y_test, mlp.predict(X_test))
plt.matshow(mat);
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
Model definition to initialize the global model
# MODEL DEFINITION
def build_model(lr=0.001, batch_size=64, local_epochs=2, warm_start=True):
model = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(50,50,),
activation='relu',
solver='sgd',
batch_size=batch_size,
learning_rate_init=lr,
max_iter=local_epochs,
early_stopping=False,
shuffle=False,
warm_start=warm_start,
tol=0.0001)
return model
6.12. Auxiliary methods for federated learning#
The following functions are used to:
get and set the NN’s weights and biases,
extract the users’ local updates by substracting the local model parameters after training from the global model parameters, and
to run a training step on the global model.
#AUXILIARY METHODS FOR FEDERATED LEARNING
# RETURN WEIGHTS AND BIASES OF A MODEL
def get_parameters(model):
return copy.deepcopy(model.coefs_), copy.deepcopy(model.intercepts_)
# SET WEIGHTS AND BIASES OF A MODEL
def set_parameters(model, weights, biases):
model.coefs_ = weights
model.intercepts_ = biases
# RETURN THE DIFFERENCE OF MODELS' WEIGHTS AND BIASES AFTER AN UPDATE
# NOTE: LEARNING RATE IS APPLIED, SO THE UPDATE IS DIFFERENT FROM THE
# GRADIENTS. IN CASE VANILLA SGD IS USED, THE GRADIENTS ARE OBTAINED
# AS (UPDATES / LEARNING_RATE)
def get_updates(model, inputs, outputs, batch_size, epochs):
w, b = get_parameters(model)
model.fit(inputs, outputs)
w_new, b_new = get_parameters(model)
weight_updates = [old - new for old,new in zip(w, w_new)]
bias_updates = [old - new for old,new in zip(b, b_new)]
return weight_updates, bias_updates
# UPDATE THE MODEL'S WEIGHTS AND PARAMETERS WITH AN UPDATE
def apply_updates(model, eta, w_new, b_new):
w, b = get_parameters(model)
new_weights = [theta - eta*delta for theta,delta in zip(w, w_new)]
new_biases = [theta - eta*delta for theta,delta in zip(b, b_new)]
set_parameters(model, new_weights, new_biases)
# FEDERATED AGGREGATION FUNCTION
def aggregate(n_layers, n_peers, f, w_updates, b_updates):
agg_w = [f([w_updates[j][i] for j in range(n_peers)], axis=0) for i in range(n_layers)]
agg_b = [f([b_updates[j][i] for j in range(n_peers)], axis=0) for i in range(n_layers)]
return agg_w, agg_b
# TRANSFORM ALL WEIGHT TENSORS TO 1D ARRAY
def flatten_weights(w_in):
h = w_in[0].reshape(-1)
for w in w_in[1:]:
h = np.append(h, w.reshape(-1))
return h
# TRANSFORM ALL BIAS TENSORS TO 1D ARRAY
def flatten_biases(b_in):
h = b_in[0].reshape(-1)
for b in b_in[1:]:
h = np.append(h, b.reshape(-1))
return h
# TRANSFORM WEIGHT AND BIAS TENSORS TO 1D ARRAY
def flatten_parameters(w_in, b_in):
w = flatten_weights(w_in)
b = flatten_biases(b_in)
return w, b
# COMPUTE EUCLIDEAN DISTANCE OF WEIGHTS
def dist_weights(w_a, w_b):
wf_a = flatten_weights(w_a)
wf_b = flatten_weights(w_b)
return euclidean(wf_a, wf_b)
# COMPUTE EUCLIDEAN DISTANCE OF BIASES
def dist_biases(b_a, b_b):
bf_a = flatten_biases(b_a)
bf_b = flatten_biases(b_b)
return euclidean(bf_a, bf_b)
# COMPUTE EUCLIDEAN DISTANCE OF WEIGHTS AND BIASES
def dist_parameters(w_a, b_a, w_b, b_b):
wf_a, bf_a = flatten_parameters(w_a, b_a)
wf_b, bf_b = flatten_parameters(w_b, b_b)
return euclidean(np.append(wf_a, bf_a), np.append(wf_b, bf_b))
6.13. Auxiliary methods for attackers#
The following to functions are used to:
flip the labels from an origin class to a target class, and
boost updates.
# AUXILIARY METHODS FOR THE ATTACKERS
def poison(labels, origin, target):
output_cat = np.where(labels == origin, target, labels)
output_cat[random.randint(0,len(labels))] = origin
return output_cat
# MULTIPLIES PARAMETERS BY SOME SCALAR BOOST
def boosting(weights, biases, boost):
w_boosted = [boost*w for w in weights]
b_boosted = [boost*b for b in biases]
return w_boosted, b_boosted
6.14. Local training#
The following function implements the local training at the clients’ side. Clients can be either good or malicious. Good peers will just run a few local training steps and return the updates. Malicious clients will also poison their data before training, and optionally boost their updates before sending them.
# Client code
def client_training(global_model, local_batch_size, n_local_rounds, features, labels, malicious, malicious_targets, malicious_boost):
# Fetch global model
local_model = copy.deepcopy(global_model)
# Local model update
if malicious:
# Malicious peer
# Modify target class labels
acts_mal = random.random() <= 1.0
if acts_mal:
labels = poison(labels, malicious_targets[i][0], malicious_targets[i][1])
# Train local model with benign and malicious data
local_weight_updates, local_bias_updates = get_updates(local_model,
features, labels,
local_batch_size, n_local_rounds)
# Boost update
if acts_mal:
local_weight_updates, local_bias_updates = boosting(local_weight_updates, local_bias_updates, malicious_boost[i])
else:
# Benign peer
# Train local model
local_weight_updates, local_bias_updates = get_updates(local_model,
inputs, outputs,
local_batch_size, n_local_rounds)
return local_weight_updates, local_bias_updates
6.15. FL Testbed#
6.15.1. Test parameters#
The following code contains the configuration of the FL tests.
The configuration includes:
Number of peers
Fraction of peers that participate in each of the global training epochs
Number of global training epochs
Number of local training epochs
Batch size for local training
Learning rate for local training
Global training rate or model substitution rate
Attack detection mechanism
None
Distance (with parameter tau)
Median
Krum (with parameter tolerance)
# TESTBED
#####################
# SYSTEM PARAMETERS #
#####################
# Number of peers
n_peers = 5
# Percentage and number of peers participating at each global training epoch
percentage_participants = 1.00
n_participants = int(n_peers * percentage_participants)
# Number of global training epochs
n_rounds = 10
# Number of local training epochs per global training epoch
n_local_rounds = 2
# Local batch size
local_batch_size = 32
# Local learning rate
local_lr = 0.001
# Global learning rate or 'gain'
model_substitution_rate = 0.25
# Attack detection / prevention mechanism = {None, 'distance', 'median', 'krum'}
discard_outliers = 'distance'
# Used in 'dist' attack detection, defines how far the outliers are (1.5 is a typical value)
tau = 1.5
# Used in 'krum' attack detection, defines how many byzantine attackers we want to defend against
tolerance=1
########################
# ATTACK CONFIGURATION #
########################
# Percentage of malicious peers
r_malicious_peers = 0.20
# Number of malicious peers (absolute or relative to total number of peers)
n_malicious_peers = int(n_peers * r_malicious_peers)
# Malicious peers
malicious_peer = range(n_malicious_peers)
# Target for coalitions
common_attack_target = ['4','7']
# Target class of the attack, per each malicious peer
malicious_targets = dict([(p, t) for p,t in zip(malicious_peer, [common_attack_target]*n_malicious_peers)])
# Boosting parameter per each malicious peer
common_malicious_boost = 10
malicious_boost = dict([(p, b) for p,b in zip(malicious_peer, [common_malicious_boost]*n_malicious_peers)])
6.15.2. Test execution#
Global model initialization
Peer initialization
Training loop
Selection of participating peers
Local training
Update collection
Attack detection
Parameter aggregation
Report accuracy
####################################
# MODEL AND NETWORK INITIALIZATION #
####################################
global_model = build_model(local_lr, local_batch_size, n_local_rounds, True)
# In Scikit-learn, an initial fit is required to build initial weight
# and bias lists
global_model.fit(X_public, y_public)
n_layers = len(global_model.coefs_)
##################
# BEGIN TRAINING #
##################
for t in range(n_rounds):
print(f'Round {t+1}.')
#sleep(1)
## SERVER SIDE #################################################################
# Initialize peer update lists
network_weight_updates = []
network_bias_updates = []
# Selection of participant peers in this global training epoch
participants = random.sample(list(range(n_peers)), n_participants)
################################################################################
## CLIENT SIDE #################################################################
for i in tqdm(participants):
# Initialization of user data
ss = int(len(X_train)/n_peers)
inputs = X_train[i*ss:i*ss+ss]
outputs = y_train[i*ss:i*ss+ss]
local_weight_updates, local_bias_updates = client_training(
global_model,
local_batch_size,
n_local_rounds,
inputs,
outputs,
i in malicious_peer,
malicious_targets,
malicious_boost
)
# Send updates to the server
network_weight_updates.append(local_weight_updates)
network_bias_updates.append(local_bias_updates)
## END OF CLIENT SIDE ##########################################################
######################################
# SERVER SIDE AGGREGATION MECHANISMS #
######################################
# No detection of outliers
if discard_outliers == None:
# Aggregate client updates
aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases = aggregate(n_layers,
n_participants,
np.mean,
network_weight_updates,
network_bias_updates)
# Apply updates to global model
apply_updates(global_model, model_substitution_rate, aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases)
# Detection of outliers via distance metric
elif discard_outliers == 'distance':
# Compute the provisional aggregate
prov_agg_w, prov_agg_b = aggregate(n_layers,
n_participants,
np.mean,
network_weight_updates,
network_bias_updates)
# Compute distances and IQR of individual updates to the provisional aggregate
distances = [dist_weights(prov_agg_w, w_i) for w_i in network_weight_updates]
q1 = np.percentile(distances, 25)
q3 = np.percentile(distances, 75)
iqr = q3 - q1
low = q1 - tau * iqr
high = q3 + tau * iqr
# Discard outliers
good_updates = [i for i,v in enumerate(distances) if low <= v <= high]
agg_participants = len(good_updates)
network_weight_updates = [w for i,w in enumerate(network_weight_updates) if i in good_updates]
network_bias_updates = [b for i,b in enumerate(network_bias_updates) if i in good_updates]
# Compute definitive update
aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases = aggregate(n_layers,
agg_participants,
np.mean,
network_weight_updates,
network_bias_updates)
# Apply update
apply_updates(global_model, model_substitution_rate, aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases)
# Robust aggregation via median
elif discard_outliers == 'median':
# Compute the aggregate as the component-wise median of local updates
aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases = aggregate(n_layers,
n_participants,
np.median,
network_weight_updates,
network_bias_updates)
# Apply update
apply_updates(global_model, model_substitution_rate, aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases)
# KRUM
elif discard_outliers == 'krum':
# First, we build a distance matrix for parameters
P = list(zip(network_weight_updates, network_bias_updates))
dist_matrix = [[dist_parameters(wi,bi,wj,bj) for wj,bj in P] for wi,bi in P]
scores = []
for index in range(len(P)):
distances_to_index = np.array(dist_matrix[index])
closest_to_index = np.argpartition(distances_to_index, n_participants-tolerance-1)[:n_participants-tolerance-1]
scores.append(np.sum(distances_to_index[closest_to_index]))
best = np.argmin(scores)
aggregated_weights = network_weight_updates[best]
aggregated_biases = network_bias_updates[best]
# Apply update
apply_updates(global_model, model_substitution_rate, aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases)
# Fallback case: no detection of outliers
else:
# Proceed as in first case
aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases = aggregate(n_layers,
n_participants,
np.mean,
network_weight_updates,
network_bias_updates)
apply_updates(global_model, model_substitution_rate, aggregated_weights, aggregated_biases)
###################
# COMPUTE METRICS #
###################
# Global model accuracy
result = global_model.predict(X_test)
score = accuracy_score(y_test, result)
print(f'Global model accuracy: {score}')
Round 1.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.47it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.7327819548872181
Round 2.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.48it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.7917293233082707
Round 3.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.49it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.833609022556391
Round 4.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.48it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.8584962406015038
Round 5.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.47it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.8734586466165414
Round 6.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.47it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.8844360902255639
Round 7.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.45it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.89
Round 8.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.41it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.8939097744360902
Round 9.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.40it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.8985714285714286
Round 10.
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 5/5 [00:03<00:00, 1.39it/s]
Global model accuracy: 0.901578947368421
# BASELINE RESULTS
mat = confusion_matrix(y_test, global_model.predict(X_test))
plt.matshow(mat);
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()